IP Address
Have you ever wondered exactly how your emails actually reach their intended destination? You’re not alone.
Enter the IP address.
Let’s take a look at what an IP address is, why they are important, the different types of IP addresses, and how you can even find out what your own IP address is.
What is an IP Address
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. IP addresses are part of the underlying core of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
IP addresses serve two main functions: identifying the host or network and providing the location of the host in the network.
This means that your laptop, tablet, and phone can all have a different IP address despite being on the same Wi-Fi.
What is the Role of an IP Address in Email Marketing?
An IP address in email marketing is basically a digital address for your emails.
When you send an email, it doesn't just magically appear in your recipient's inbox.
Think of the IP address as a return address on a physical letter. It tells the recipient (and their email server) where the email is coming from.
In email marketing, your IP address can affect your sender reputation. A good sender reputation will lead to more of your emails being delivered successfully. On the flip side, a poor reputation (this can be linked to shared IP addresses with spammers or due to your own negative sending behavior) can lead to your emails being blocked or landing in the spam folder.
Key Considerations for Managing IP Addresses in Email Marketing
Successfully monitoring and managing your IP address will go a long way in your email marketing efforts. Let’s take a look at a few key things to consider along the way:
Dedicated vs. Shared IP Addresses: You might use a shared IP address when starting out in email marketing. It's cost-effective but comes with the risk of sharing it with other senders, potentially bad actors that would negatively affect your sender reputation. As your email marketing grows you may consider moving to a dedicated IP address, which you don't share with other senders. This gives you more control over your sender reputation.
IP Warming: When you start using a new IP address, you should gradually increase the volume of emails sent to establish a good sender reputation. Sending large volumes of emails on day one can trigger spam filters.
Monitor Your IP Reputation: Regularly check your IP address against blacklists and monitor delivery rates.
Consistency in Email Volume: Keep your email send volumes consistent. Spikes in volume can appear suspicious and affect your sender reputation.
Maintaining Good Email Practices: To protect your IP reputation, maintain best practices in email marketing. This includes having a clear opt-in process, segmenting your audience, personalizing content, and regularly cleaning your email list.
By understanding and managing your IP address effectively you can ensure better deliverability and overall success in your email marketing campaigns. But like all things in email marketing, this is simply one of the many levers that you will need to be aware of.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 IP Addresses?
The most common format of an IP address is IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), which consists of four numbers separated by dots (example: 192.168.1.1.). Each number can range from 0 to 255, which means that there are over 4 billion unique addresses possible.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is a newer version of IP address that was developed to address the shortage of IPs in IPv4. IPv6 consists of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits (example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
IPv6 significantly expands the number of available addresses.
IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are not interchangeable, and the move towards IPv6 is ongoing due to the increasing number of devices requiring IP addresses.
Different Types of IP Addresses
Outside of IPv4 and IPv6, there are other types of IP addresses that you should be aware of.
Public IP Address: Accessible over the internet, unique and identifiable. Required for any device that directly communicates over the internet.
Private IP Address: Used within a local network and allows for secure and isolated communication within a network.
Shared IP Address: Multiple entities share a single IP address, commonly seen in shared hosting environments. Cheaper for email marketers but poses risks of shared reputation.
Dedicated IP Address: Exclusively assigned to a single entity which offers stability and control. This is beneficial for businesses with high email communication needs that can’t risk being affected by other bad actors on a shared IP address.
Dynamic IP Address: Temporarily assigned and subject to change. Common in residential internet connections.
Static IP Address: Permanent and consistent. These are typically used for hosting servers or other equipment requiring constant addresses.
How can I find my IP Address?
All this IP address talk have you curious as to what yours is? There are a few ways that you can find your own IP address.
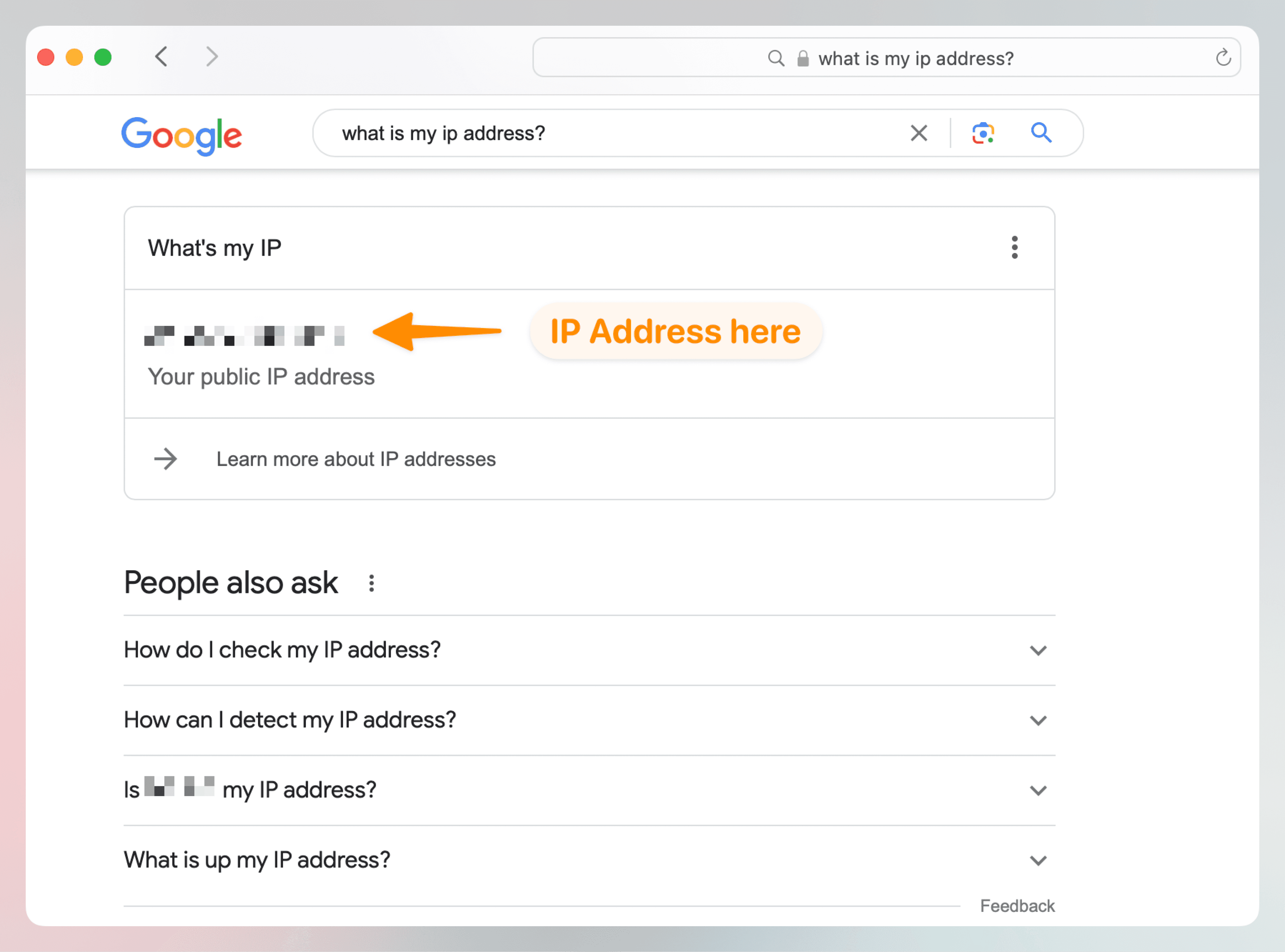
There are countless websites that can tell you your IP address. Even Googling “what is my IP address” will give you a quick answer.
If you’re on an iPhone, you can head to your settings, click on Wi-Fi, then click the little “i” to the right of your Wi-Fi name.
If you’re on Android, head to your settings, click on connections,click on Wi-Fi, then click the gear icon.
Key takeaways
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network.
IP addresses are a key part of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
An IP address is critical to the long term success (or failure) for email marketers.
There are many different types of IP address (public, private, shared, dedicated, dynamic, static)
It is possible for bad actors to negatively impact your email deliverability if you’re sending from a shared IP address. It is important to monitor your sending reputation so that you know if you might be affected.
Have you ever wondered exactly how your emails actually reach their intended destination? You’re not alone.
Enter the IP address.
Let’s take a look at what an IP address is, why they are important, the different types of IP addresses, and how you can even find out what your own IP address is.
What is an IP Address
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. IP addresses are part of the underlying core of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
IP addresses serve two main functions: identifying the host or network and providing the location of the host in the network.
This means that your laptop, tablet, and phone can all have a different IP address despite being on the same Wi-Fi.
What is the Role of an IP Address in Email Marketing?
An IP address in email marketing is basically a digital address for your emails.
When you send an email, it doesn't just magically appear in your recipient's inbox.
Think of the IP address as a return address on a physical letter. It tells the recipient (and their email server) where the email is coming from.
In email marketing, your IP address can affect your sender reputation. A good sender reputation will lead to more of your emails being delivered successfully. On the flip side, a poor reputation (this can be linked to shared IP addresses with spammers or due to your own negative sending behavior) can lead to your emails being blocked or landing in the spam folder.
Key Considerations for Managing IP Addresses in Email Marketing
Successfully monitoring and managing your IP address will go a long way in your email marketing efforts. Let’s take a look at a few key things to consider along the way:
Dedicated vs. Shared IP Addresses: You might use a shared IP address when starting out in email marketing. It's cost-effective but comes with the risk of sharing it with other senders, potentially bad actors that would negatively affect your sender reputation. As your email marketing grows you may consider moving to a dedicated IP address, which you don't share with other senders. This gives you more control over your sender reputation.
IP Warming: When you start using a new IP address, you should gradually increase the volume of emails sent to establish a good sender reputation. Sending large volumes of emails on day one can trigger spam filters.
Monitor Your IP Reputation: Regularly check your IP address against blacklists and monitor delivery rates.
Consistency in Email Volume: Keep your email send volumes consistent. Spikes in volume can appear suspicious and affect your sender reputation.
Maintaining Good Email Practices: To protect your IP reputation, maintain best practices in email marketing. This includes having a clear opt-in process, segmenting your audience, personalizing content, and regularly cleaning your email list.
By understanding and managing your IP address effectively you can ensure better deliverability and overall success in your email marketing campaigns. But like all things in email marketing, this is simply one of the many levers that you will need to be aware of.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 IP Addresses?
The most common format of an IP address is IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), which consists of four numbers separated by dots (example: 192.168.1.1.). Each number can range from 0 to 255, which means that there are over 4 billion unique addresses possible.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is a newer version of IP address that was developed to address the shortage of IPs in IPv4. IPv6 consists of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits (example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
IPv6 significantly expands the number of available addresses.
IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are not interchangeable, and the move towards IPv6 is ongoing due to the increasing number of devices requiring IP addresses.
Different Types of IP Addresses
Outside of IPv4 and IPv6, there are other types of IP addresses that you should be aware of.
Public IP Address: Accessible over the internet, unique and identifiable. Required for any device that directly communicates over the internet.
Private IP Address: Used within a local network and allows for secure and isolated communication within a network.
Shared IP Address: Multiple entities share a single IP address, commonly seen in shared hosting environments. Cheaper for email marketers but poses risks of shared reputation.
Dedicated IP Address: Exclusively assigned to a single entity which offers stability and control. This is beneficial for businesses with high email communication needs that can’t risk being affected by other bad actors on a shared IP address.
Dynamic IP Address: Temporarily assigned and subject to change. Common in residential internet connections.
Static IP Address: Permanent and consistent. These are typically used for hosting servers or other equipment requiring constant addresses.
How can I find my IP Address?
All this IP address talk have you curious as to what yours is? There are a few ways that you can find your own IP address.
There are countless websites that can tell you your IP address. Even Googling “what is my IP address” will give you a quick answer.

If you’re on an iPhone, you can head to your settings, click on Wi-Fi, then click the little “i” to the right of your Wi-Fi name.
If you’re on Android, head to your settings, click on connections,click on Wi-Fi, then click the gear icon.
Key takeaways
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network.
IP addresses are a key part of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
An IP address is critical to the long term success (or failure) for email marketers.
There are many different types of IP address (public, private, shared, dedicated, dynamic, static)
It is possible for bad actors to negatively impact your email deliverability if you’re sending from a shared IP address. It is important to monitor your sending reputation so that you know if you might be affected.
Ready to send better email?
Loops is a better way to send product, marketing, and transactional email for your SaaS company.
Have you ever wondered exactly how your emails actually reach their intended destination? You’re not alone.
Enter the IP address.
Let’s take a look at what an IP address is, why they are important, the different types of IP addresses, and how you can even find out what your own IP address is.
What is an IP Address
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. IP addresses are part of the underlying core of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
IP addresses serve two main functions: identifying the host or network and providing the location of the host in the network.
This means that your laptop, tablet, and phone can all have a different IP address despite being on the same Wi-Fi.
What is the Role of an IP Address in Email Marketing?
An IP address in email marketing is basically a digital address for your emails.
When you send an email, it doesn't just magically appear in your recipient's inbox.
Think of the IP address as a return address on a physical letter. It tells the recipient (and their email server) where the email is coming from.
In email marketing, your IP address can affect your sender reputation. A good sender reputation will lead to more of your emails being delivered successfully. On the flip side, a poor reputation (this can be linked to shared IP addresses with spammers or due to your own negative sending behavior) can lead to your emails being blocked or landing in the spam folder.
Key Considerations for Managing IP Addresses in Email Marketing
Successfully monitoring and managing your IP address will go a long way in your email marketing efforts. Let’s take a look at a few key things to consider along the way:
Dedicated vs. Shared IP Addresses: You might use a shared IP address when starting out in email marketing. It's cost-effective but comes with the risk of sharing it with other senders, potentially bad actors that would negatively affect your sender reputation. As your email marketing grows you may consider moving to a dedicated IP address, which you don't share with other senders. This gives you more control over your sender reputation.
IP Warming: When you start using a new IP address, you should gradually increase the volume of emails sent to establish a good sender reputation. Sending large volumes of emails on day one can trigger spam filters.
Monitor Your IP Reputation: Regularly check your IP address against blacklists and monitor delivery rates.
Consistency in Email Volume: Keep your email send volumes consistent. Spikes in volume can appear suspicious and affect your sender reputation.
Maintaining Good Email Practices: To protect your IP reputation, maintain best practices in email marketing. This includes having a clear opt-in process, segmenting your audience, personalizing content, and regularly cleaning your email list.
By understanding and managing your IP address effectively you can ensure better deliverability and overall success in your email marketing campaigns. But like all things in email marketing, this is simply one of the many levers that you will need to be aware of.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 IP Addresses?
The most common format of an IP address is IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), which consists of four numbers separated by dots (example: 192.168.1.1.). Each number can range from 0 to 255, which means that there are over 4 billion unique addresses possible.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is a newer version of IP address that was developed to address the shortage of IPs in IPv4. IPv6 consists of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits (example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
IPv6 significantly expands the number of available addresses.
IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are not interchangeable, and the move towards IPv6 is ongoing due to the increasing number of devices requiring IP addresses.
Different Types of IP Addresses
Outside of IPv4 and IPv6, there are other types of IP addresses that you should be aware of.
Public IP Address: Accessible over the internet, unique and identifiable. Required for any device that directly communicates over the internet.
Private IP Address: Used within a local network and allows for secure and isolated communication within a network.
Shared IP Address: Multiple entities share a single IP address, commonly seen in shared hosting environments. Cheaper for email marketers but poses risks of shared reputation.
Dedicated IP Address: Exclusively assigned to a single entity which offers stability and control. This is beneficial for businesses with high email communication needs that can’t risk being affected by other bad actors on a shared IP address.
Dynamic IP Address: Temporarily assigned and subject to change. Common in residential internet connections.
Static IP Address: Permanent and consistent. These are typically used for hosting servers or other equipment requiring constant addresses.
How can I find my IP Address?
All this IP address talk have you curious as to what yours is? There are a few ways that you can find your own IP address.
There are countless websites that can tell you your IP address. Even Googling “what is my IP address” will give you a quick answer.

If you’re on an iPhone, you can head to your settings, click on Wi-Fi, then click the little “i” to the right of your Wi-Fi name.
If you’re on Android, head to your settings, click on connections,click on Wi-Fi, then click the gear icon.
Key takeaways
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network.
IP addresses are a key part of the internet, allowing different devices to find and communicate with each other.
An IP address is critical to the long term success (or failure) for email marketers.
There are many different types of IP address (public, private, shared, dedicated, dynamic, static)
It is possible for bad actors to negatively impact your email deliverability if you’re sending from a shared IP address. It is important to monitor your sending reputation so that you know if you might be affected.